最近在尝试把 Rust 写的应用交叉编译到 RISC-V 的机器上。
目标机器是 RISC-V 架构,系统使用 buildroot,libc 为 musl。
看起来我们可以直接编译一个 musl 版本的程序,就能解决,而且 rust 支持 musl 的 target
标准的 C 库实现
1973 年汤普逊和里奇用 C 语言重写了 Unix
由于整个 Unix/Linux 都是建立在 C 之上,几乎所有的程序都依赖了 libc
在 Linux 下 libc 有四个实现:
glibc, musl libc, uClibc/uClibc-ng, Bionic C
glibc 基本上就是事实的标准musl libc 容器或者嵌入式设备,静态编译用的比较多uClibc/uClibc-ng (uClibc已经停止维护了, uClibc-ng是新的版本)主要用于无 MMU (Memory Management Unit) 的设备,也有非常少量了 Linux 用了 uClibc(比如旧版本的 OpenWRT 和一些特殊的硬件,新版本用了 musl libc)Bionic C 主要用于 Android,一般不把它算在 Linux 的生态里
如何判断是否为静态编译 file这是一个比较高级的命令,通过很多因素判断,还是非常准确的
1 2 % file $(which gcc) /usr/bin/gcc: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=d68af36149454ddf51e22ad93db29f583c51f70b, for GNU/Linux 4.4.0, stripped
在 Linux 下的可执行文件时 ELF (Executable and Linkable Format) 格式,ELF 是一种用于可执行文件、目标代码、共享库和核心转储(core dump)的标准文件格式
我们先来写一个最简单的程序验证一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 cat > hello.c << EOF #include <stdio.h> int main() { printf("Hello, World!\r\n"); return 0; } EOF
1 2 3 4 5 % gcc hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-gnu % ./c-hello-gcc-gnu Hello, World! % file -b c-hello-gcc-gnu ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=6169fdfc99a343c23b9d349da437b313e09254e3, for GNU/Linux 4.4.0, not stripped
通过 file 命令,我们可以看到 dynamically linked 标识它是动态链接,interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 是动态链接的加载器
我们需要先了解一下,动态链接的工作流程,执行会去通过 interpreter 字段记录的位置找 ld (动态链接装载器),然后由 ld 加载 Dynamic section 里面记录动态链接
ldd 命令 我们可以通过 ldd (List Dynamic Dependencies)来找动态链接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 % gcc hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-gnu % ./c-hello-gcc-gnu Hello, World! % file -b c-hello-gcc-gnu ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=6169fdfc99a343c23b9d349da437b313e09254e3, for GNU/Linux 4.4.0, not stripped % ldd c-hello-gcc-gnu linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007b07aeba6000) libc.so.6 => /usr/lib/libc.so.6 (0x00007b07ae999000) /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 => /usr/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007b07aeba8000)
加上静态编译参数,ldd 没有发现动态链接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 % gcc -static hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-gnu-static % ./c-hello-gcc-gnu-static Hello, World! % file -b c-hello-gcc-gnu-static ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), statically linked, BuildID[sha1]=532829a15c17e744e340e6ab081ace670137dfd2, for GNU/Linux 4.4.0, not stripped % ldd c-hello-gcc-gnu-static not a dynamic executable
当然 ldd 其实非常的不靠谱,比如就没法判断这个
1 2 3 4 5 % musl-gcc hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-musl % file -b c-hello-gcc-musl ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-musl-x86_64.so.1, not stripped % ldd c-hello-gcc-musl ./c-hello-gcc-musl: error while loading shared libraries: /usr/lib/libc.so: invalid ELF header
当然这是由于 ldd 的工作原理决定的,ldd 要去执行程序,执行到 ld 的位置停下,输出动态链接的部分,如果这个程序本身是完全静态,不依赖于 ld,ldd 是完全无效的,对于找不到 ld 和跨架构的情况也是完全不可用
1 2 $ cat $(which ldd) | wc -l 191
ldd 本身就是个 shell 脚本,添加了几个环境变量
直接执行 LD_TRACE_LOADED_OBJECTS=1 ./c-hello-gcc-gnu 效果是一样的
1 2 3 4 % LD_TRACE_LOADED_OBJECTS=1 ./c-hello-gcc-gnu linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007783dc6cf000) libc.so.6 => /usr/lib/libc.so.6 (0x00007783dc4c7000) /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007783dc6d1000)
ldd 只用来判断当前系统可以执行的动态程序用了那些动态依赖
readelf readelf 属于 binutils 提供的工具,可以读 ELF 格式里面的内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 % readelf -h c-hello-gcc-gnu ELF Header: Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 Class: ELF64 Data: 2's complement, little endian Version: 1 (current) OS/ABI: UNIX - System V ABI Version: 0 Type: DYN (Position-Independent Executable file) Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64 Version: 0x1 Entry point address: 0x1040 Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file) Start of section headers: 13496 (bytes into file) Flags: 0x0 Size of this header: 64 (bytes) Size of program headers: 56 (bytes) Number of program headers: 14 Size of section headers: 64 (bytes) Number of section headers: 30 Section header string table index: 29
我们可以通过 Type: DYN (Position-Independent Executable file) 来判断是动态链接,但是这种判读也不准确
如果把 PIE 去掉,类型和静态链接完全一样,倒是可以判断是否有 PIE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 % gcc hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-gnu % readelf -h c-hello-gcc-gnu | grep Type Type: DYN (Position-Independent Executable file) % gcc -no-pie hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-gnu-nopie % readelf -h c-hello-gcc-gnu-nopie | grep Type Type: EXEC (Executable file) % gcc -static hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-gnu-static % readelf -h c-hello-gcc-gnu-static | grep Type Type: EXEC (Executable file) % gcc -static-pie hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-gnu-static-pie % readelf -h c-hello-gcc-gnu-static-pie | grep Type Type: DYN (Position-Independent Executable file)
ELF 格式有两个 header,readelf -h 是看文件的 header,readelf -l 是看程序的 header
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 % readelf -l c-hello-gcc-gnu Elf file type is DYN (Position-Independent Executable file) Entry point 0x1040 There are 14 program headers, starting at offset 64 Program Headers: Type Offset VirtAddr PhysAddr FileSiz MemSiz Flags Align PHDR 0x0000000000000040 0x0000000000000040 0x0000000000000040 0x0000000000000310 0x0000000000000310 R 0x8 INTERP 0x00000000000003b4 0x00000000000003b4 0x00000000000003b4 0x000000000000001c 0x000000000000001c R 0x1 [Requesting program interpreter: /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2] LOAD 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000640 0x0000000000000640 R 0x1000 LOAD 0x0000000000001000 0x0000000000001000 0x0000000000001000 0x0000000000000161 0x0000000000000161 R E 0x1000 LOAD 0x0000000000002000 0x0000000000002000 0x0000000000002000 0x00000000000000d4 0x00000000000000d4 R 0x1000 LOAD 0x0000000000002dd0 0x0000000000003dd0 0x0000000000003dd0 0x0000000000000248 0x0000000000000250 RW 0x1000 DYNAMIC 0x0000000000002de0 0x0000000000003de0 0x0000000000003de0 0x00000000000001e0 0x00000000000001e0 RW 0x8 NOTE 0x0000000000000350 0x0000000000000350 0x0000000000000350 0x0000000000000040 0x0000000000000040 R 0x8 NOTE 0x0000000000000390 0x0000000000000390 0x0000000000000390 0x0000000000000024 0x0000000000000024 R 0x4 NOTE 0x00000000000020b4 0x00000000000020b4 0x00000000000020b4 0x0000000000000020 0x0000000000000020 R 0x4 GNU_PROPERTY 0x0000000000000350 0x0000000000000350 0x0000000000000350 0x0000000000000040 0x0000000000000040 R 0x8 GNU_EH_FRAME 0x0000000000002014 0x0000000000002014 0x0000000000002014 0x0000000000000024 0x0000000000000024 R 0x4 GNU_STACK 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 RW 0x10 GNU_RELRO 0x0000000000002dd0 0x0000000000003dd0 0x0000000000003dd0 0x0000000000000230 0x0000000000000230 R 0x1 Section to Segment mapping: Segment Sections... 00 01 .interp 02 .note.gnu.property .note.gnu.build-id .interp .gnu.hash .dynsym .dynstr .gnu.version .gnu.version_r .rela.dyn .rela.plt 03 .init .plt .text .fini 04 .rodata .eh_frame_hdr .eh_frame .note.ABI-tag 05 .init_array .fini_array .dynamic .got .got.plt .data .bss 06 .dynamic 07 .note.gnu.property 08 .note.gnu.build-id 09 .note.ABI-tag 10 .note.gnu.property 11 .eh_frame_hdr 12 13 .init_array .fini_array .dynamic .got
我们可以通过 INTERP 的 /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 来判断它使用了动态链接,具体那些做了动态链接,我们可以使用 readelf -d 来看 Dynamic section 里面的内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 % readelf -d c-hello-gcc-gnu Dynamic section at offset 0x2de0 contains 26 entries: Tag Type Name/Value 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libc.so.6] 0x000000000000000c (INIT) 0x1000 0x000000000000000d (FINI) 0x1154 0x0000000000000019 (INIT_ARRAY) 0x3dd0 0x000000000000001b (INIT_ARRAYSZ) 8 (bytes) 0x000000000000001a (FINI_ARRAY) 0x3dd8 0x000000000000001c (FINI_ARRAYSZ) 8 (bytes) 0x000000006ffffef5 (GNU_HASH) 0x3d0 0x0000000000000005 (STRTAB) 0x498 0x0000000000000006 (SYMTAB) 0x3f0 0x000000000000000a (STRSZ) 141 (bytes) 0x000000000000000b (SYMENT) 24 (bytes) 0x0000000000000015 (DEBUG) 0x0 0x0000000000000003 (PLTGOT) 0x3fe8 0x0000000000000002 (PLTRELSZ) 24 (bytes) 0x0000000000000014 (PLTREL) RELA 0x0000000000000017 (JMPREL) 0x628 0x0000000000000007 (RELA) 0x568 0x0000000000000008 (RELASZ) 192 (bytes) 0x0000000000000009 (RELAENT) 24 (bytes) 0x000000006ffffffb (FLAGS_1) Flags: PIE 0x000000006ffffffe (VERNEED) 0x538 0x000000006fffffff (VERNEEDNUM) 1 0x000000006ffffff0 (VERSYM) 0x526 0x000000006ffffff9 (RELACOUNT) 3 0x0000000000000000 (NULL) 0x0
静态链接,没有 Dynamic section,所以里面没有内容,所以也可以通过这个来判断是否是动态链接?当然,这个不行,还有一种特殊情况
1 2 3 % readelf -d c-hello-gcc-gnu-static There is no dynamic section in this file.
PIE PIE(Position-Independent Executable,位置无关可执行文件)是一种安全技术,它使可执行程序在内存中的加载地址随机化,从而增强系统的安全性。运行时由动态链接器配合操作系统随机化加载地址,目前很多编译器默认会开 PIE。
PIE 本质上是利用 ld 完成的随机加载,静态编译没有 ld ,需要把 ld 的 PIE 相关的功能也打包进去。
另外 PIE 的部分符号信息是写在 Dynamic section 里面的,所以,静态链接 PIE 会有 Dynamic section 里会有一些符号信息
-static 和 -pie 在一起时,有一些天然的互斥,不过目前的编译器都可以做到
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 % gcc -static-pie hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-gnu-static-pie % file -b c-hello-gcc-gnu-static-pie ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), static-pie linked, BuildID[sha1]=2a89b311b755433561c90ed642fdb44756e5063b, for GNU/Linux 4.4.0, not stripped % readelf -d c-hello-gcc-gnu-static-pie Dynamic section at offset 0xafd68 contains 22 entries: Tag Type Name/Value 0x000000000000000c (INIT) 0x7000 0x000000000000000d (FINI) 0x82790 0x0000000000000019 (INIT_ARRAY) 0xabc60 0x000000000000001b (INIT_ARRAYSZ) 16 (bytes) 0x000000000000001a (FINI_ARRAY) 0xabc70 0x000000000000001c (FINI_ARRAYSZ) 16 (bytes) 0x000000006ffffef5 (GNU_HASH) 0x380 0x0000000000000005 (STRTAB) 0x3b8 0x0000000000000006 (SYMTAB) 0x3a0 0x000000000000000a (STRSZ) 1 (bytes) 0x000000000000000b (SYMENT) 24 (bytes) 0x0000000000000015 (DEBUG) 0x0 0x0000000000000003 (PLTGOT) 0xaffe8 0x0000000000000002 (PLTRELSZ) 432 (bytes) 0x0000000000000014 (PLTREL) RELA 0x0000000000000017 (JMPREL) 0x6ae0 0x0000000000000007 (RELA) 0x3c0 0x0000000000000008 (RELASZ) 26400 (bytes) 0x0000000000000009 (RELAENT) 24 (bytes) 0x000000006ffffffb (FLAGS_1) Flags: PIE 0x000000006ffffff9 (RELACOUNT) 1096 0x0000000000000000 (NULL) 0x0
patchelf移花接木,使用 patchelf 工具去改变动态链接
你有没有想过,既然差距就在 glibc 和 musl 的 ld 和 libc 位置不同,那我能不能直接修改 ELF 的位置,来把原本是动态链接 glibc 的程序改成动态链接 musl
但 glibc 和 musl 只有核心部分兼容,对于只用标准 c 和 posix c 的程序是可以兼容的,但 musl力求精简和标准 glibc 兼容更好也更为庞大,把动态链接 musl 改成动态链接 glibc 的成功率更高一些,不过这种改法没什么实际的应用价值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 % gcc hello.c -o c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf % readelf -l c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf | grep interpreter [Requesting program interpreter: /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2] % readelf -d c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf | grep NEEDED 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libc.so.6] % patchelf --set-interpreter /lib/ld-musl-x86_64.so.1 c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf % patchelf --replace-needed libc.so.6 libc.so c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf % ./c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf Hello, World! % readelf -l c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf | grep interpreter [Requesting program interpreter: /lib/ld-musl-x86_64.so.1] % readelf -d c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf | grep NEEDED 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libc.so]
不过还是能看到好多有问题的地方的,但程序能跑(
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 % hexdump -C c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf * 00005000 00 70 75 74 73 00 5f 5f 6c 69 62 63 5f 73 74 61 |.puts.__libc_sta| 00005010 72 74 5f 6d 61 69 6e 00 5f 5f 63 78 61 5f 66 69 |rt_main.__cxa_fi| 00005020 6e 61 6c 69 7a 65 00 6c 69 62 63 2e 73 6f 2e 36 |nalize.libc.so.6| 00005030 00 47 4c 49 42 43 5f 32 2e 32 2e 35 00 47 4c 49 |.GLIBC_2.2.5.GLI| 00005040 42 43 5f 32 2e 33 34 00 5f 49 54 4d 5f 64 65 72 |BC_2.34._ITM_der| 00005050 65 67 69 73 74 65 72 54 4d 43 6c 6f 6e 65 54 61 |egisterTMCloneTa| 00005060 62 6c 65 00 5f 5f 67 6d 6f 6e 5f 73 74 61 72 74 |ble.__gmon_start| 00005070 5f 5f 00 5f 49 54 4d 5f 72 65 67 69 73 74 65 72 |__._ITM_register| 00005080 54 4d 43 6c 6f 6e 65 54 61 62 6c 65 00 6c 69 62 |TMCloneTable.lib| 00005090 63 2e 73 6f 00 00 00 00 00 |c.so.....| 00005099
不要用 patchelf 来移植不同的 libc,本身 glibc 和 musl 就差距很大,glibc 功能非常庞大
Go 的编译 Golang 不依赖系统的 libc,通过两个变量直接交叉编译出其他平台的程序,非常的方便
1 GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build
但 CGO 的情况还是可能依赖 libc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 cat > hello.go << EOF package main import "fmt" func main() { fmt.Println("hello world!") } EOF
CGO_ENABLED 主要是用来禁用 CGO 的,过于简单的完全不依赖 CGO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 % CGO_ENABLED=0 go build -o go-hello-0 ./hello.go % file -b go-hello-0 ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, BuildID[sha1]=b5b7d5fb91fa0881908a29fb762f71d1244b808a, with debug_info, not stripped % CGO_ENABLED=1 go build -o go-hello-1 ./hello.go % file -b go-hello-1 ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, BuildID[sha1]=6acc631714b8e9f1ece35c8a2c0cafeee876ae30, with debug_info, not stripped
比如我们使用 std 的 net 包,默认会使用 CGO,我们禁用 CGO 来静态编译
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 cat > lookup.go << EOF package main import ( "fmt" "net" ) func main() { addrs, err := net.LookupHost("baidu.com") if err != nil { panic(err) } fmt.Println("Baidu IPs:", addrs) } EOF
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 % CGO_ENABLED=0 go build -o go-lookup-0 ./lookup.go % file -b ./go-lookup-0 ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, BuildID[sha1]=0c269da87124d8d01065f131f3527b4e8a0044fe, with debug_info, not stripped % CGO_ENABLED=1 go build -o go-lookup-1 ./lookup.go % file -b ./go-lookup-1 ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=48cc551954f4de00d378dfac57065055a4f4a28c, with debug_info, not stripped % ldd go-lookup-1 linux-vdso.so.1 (0x000078aa44203000) libresolv.so.2 => /usr/lib/libresolv.so.2 (0x000078aa441db000) libc.so.6 => /usr/lib/libc.so.6 (0x000078aa43fe9000) /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 => /usr/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x000078aa44205000)
Zig 的编译 Zig 是一门开源的、静态类型的、跨平台的系统编程语言,甚至集成了 c/c++ 的编译器。当然我们可以把它当成 c 的编译器来用
zig cc 会在 *-linux-gnu 编译成动态链接,在 *-linux-musl 编译成静态链接
1 2 3 % zig cc -target x86_64-linux-gnu hello.c -o c-hello-zig-gnu % file -b c-hello-zig-gnu ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.0.0, with debug_info, not stripped
1 2 3 % zig cc -target x86_64-linux-musl hello.c -o c-hello-zig-musl % file -b c-hello-zig-musl ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, with debug_info, not stripped
我们知道如果使用 gcc / clang 交叉编译时,每个平台都需要单独的交叉编译工具链
比如 arm64 需要 aarch64-linux-gnu-gc , Risc-V 需要 riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc
zig 和 go 一样可以编译所有支持的平台,非常的方便,不过 zig 还有内置 C 的编译工具链,交叉编译非常的方便
Rust 的编译 rust 自己交叉编译,但 Rust 是依赖 libc 的。rust 交叉编译仍然需要对应平台的 C 编译器
对于每个平台我们都需要单独安装对应的 C 的工具链,更确切的说是,rust 目前自己没有 ld。rust 自己的编译器只能编译到 .o 文件,需要其他的 ld 来生成对应平台的 ELF
zig 和 rust rust 没法处理 ld 和 c 扩展的交叉编译问题,zig 有很好交叉编译工具链,集成 C 编译器
这时候我们可以考虑使用 rust 和 zig 一起用
zig cc 是子命令,所以我们需要实现一个简单的包装器 zig.sh
1 2 #!/bin/sh zig cc -target riscv64-linux-musl $@
我们可以直接指定环境变量使用这个 Linker
1 2 % CARGO_TARGET_RISCV64GC_UNKNOWN_LINUX_MUSL_LINKER="./zig.sh" \ cargo build --release --target riscv64gc-unknown-linux-musl
也可以修改一下编译配置 .cargo/config.toml
1 2 [target.riscv64gc-unknown-linux-musl] linker = "./zig.sh"
很棒,完全的静态链接
1 2 file -b rust-hello ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, UCB RISC-V, RVC, double-float ABI, version 1 (SYSV), static-pie linked, stripped
这只是处理了 Linker,手动太麻烦了,而且有 C 扩展还需要其他配置
这里有个 cargo 的插件 cargo-zigbuild ,帮你把这些都处理好了
1 2 3 4 % cargo zigbuild --release --target riscv64gc-unknown-linux-musl % file -b rust-hello ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, UCB RISC-V, RVC, double-float ABI, version 1 (SYSV), static-pie linked, stripped
zig 虽然好用,兼容性也很好,但并不一定能处理全部的情况?
cross-rs rust 交叉编译神器 cross-rs,使用 Docker 构建交叉编译环境,在容器里面配好了 C 的交叉编译工具链
但是 cross 目前不支持 riscv64gc-unknown-linux-musl 我们来加一个,这个 PR 已经合了 cross-rs#1664
顺便分享一下给 cross-rs 加新的 target 踩的坑。cross-rs 其实是个非常老的项目,目前有两套环境构建方法。一个是比较常规的编译安装 gcc,另一个用 crosstool-ng 来配环境
编译 musl 版本也用 gcc 来编译,但需要配置的东西比较多,官方提供了一个叫 musl-gcc 的 warp。当然 binutils 也 warp 过,musl 提供一个 make 脚本帮助你来编译 musl-gcc。但是 musl-cross-make 吸收了几个关于 binutils 的 patch,然后有 break change。这个 patch 非常庞大,很难迁移
这就导致 binutils 比较旧,它的 ld 没法适配新的 RISC-V 的格式。当然自己用可以直接去升级 binutils。那几个 patch 没有关于 RISC-V 相关的。推动这个 musl-cross-make 升级也很难,除非说服维护者放弃那几个 patch
最终还是选择和 crosstool-ng 来安装容器环境
静态编译 libc Rust 的程序是依赖 libc 的,官方提供了 gnu 和 musl 版本的编译器。glibc 和 musl 都是两种情况默认都是动态链接。对,musl 默认也是动态链接
我们需要传递一些 CRT (C runtime) 参数才能静态编译 libc
1 RUSTFLAGS="-C target-feature=+crt-static" cargo build --release
也可以在 .cargo/config.toml 里设置
1 2 [target.riscv64gc-unknown-linux-gnu] rustflags = ["-C" , "target-feature=+crt-static" ]
我们可以编译出 glibc 静态编译的版本,也可以有 musl 静态编译的版本。实际对比体积几乎无区别。但是,可别忘了 glibc 是 LGPL 许可证,对于静态链接是有法律上的限制
体积对比 各工具链编译出的体积的对比参考
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 16K c-hello-gcc-gnu 21K c-hello-gcc-gnu-elf 16K c-hello-gcc-gnu-nopie 16K c-hello-gcc-gnu-pie 760K c-hello-gcc-gnu-static 801K c-hello-gcc-gnu-static-pie 15K c-hello-gcc-musl 18K c-hello-gcc-musl-static 15K c-hello-gcc-musl-static-pie 7.9K c-hello-zig-gnu 9.4K c-hello-zig-gnu-aarch64 111K c-hello-zig-musl 1.8M c-hello-zig-musl-riscv64 2.2M go-hello-0 2.2M go-hello-1 3.0M go-lookup-0 3.1M go-lookup-1 423K riscv64-rust-hello-gcc-gnu 435K riscv64-rust-hello-gcc-gnu-elf 421K riscv64-rust-hello-gcc-musl 432K rust-hello-gcc-gnu 1.5M rust-hello-gcc-gnu-static 535K rust-hello-gcc-musl 535K rust-hello-gcc-musl-static 384K rust-hello-zig-gnu 393K rust-hello-zig-musl 24M rust-live777-gcc-gnu 25M rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf 24M rust-live777-gcc-musl 30 sh-hello.sh
patchelf rust 应用 测试的 RISC-V 环境
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 % cat /etc/os-release NAME=Buildroot VERSION=-g1fcc2fd40 ID=buildroot VERSION_ID=2023.11.2 PRETTY_NAME="Buildroot 2023.11.2" % uname -a Linux licheervnano-1d6b 5.10.4-tag- % cat /etc/os-release NAME=Buildroot VERSION=-g1fcc2fd40 ID=buildroot VERSION_ID=2023.11.2 PRETTY_NAME="Buildroot 2023.11.2" % ls /lib/ld-musl-*.so.1 /lib/ld-musl-riscv64-sf.so.1 /lib/ld-musl-riscv64v0p7_xthead.so.1 /lib/ld-musl-riscv64xthead-sf.so.1 /lib/ld-musl-riscv64.so.1 /lib/ld-musl-riscv64v_xthead.so.1 /lib/ld-musl-riscv64xthead.so.1
patchelf rust 的 hello world,把动态链接 glibc 的改成动态链接 musl
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 % cp target/riscv64gc-unknown-linux-gnu/release/build-static rust-hello-gcc-gnu-elf % cp target/riscv64gc-unknown-linux-gnu/release/build-static rust-hello-gcc-gnu % cp target/riscv64gc-unknown-linux-musl/release/build-static rust-hello-gcc-musl % readelf -d rust-hello-gcc-gnu-elf | grep NEEDED 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libgcc_s.so.1] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libc.so] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [ld-linux-riscv64-lp64d.so.1] % patchelf --set-interpreter /lib/ld-musl-riscv64.so.1 rust-hello-gcc-gnu-elf % patchelf --replace-needed libc.so.6 libc.so rust-hello-gcc-gnu-elf % patchelf --replace-needed ld-linux-riscv64-lp64d.so.1 ld-musl-riscv64.so.1 rust-hello-gcc-gnu-elf % readelf -d rust-hello-gcc-gnu-elf | grep NEEDED 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libgcc_s.so.1] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libc.so] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [ld-musl-riscv64.so.1]
移花接木大法搞出来的 rust-hello-gcc-gnu-elf 是可以正常运行的
1 2 3 4 5 6 % ./rust-hello-gcc-gnu -sh: ./rust-hello-gcc-gnu: not found % ./rust-hello-gcc-gnu-elf Hello, world! % ./rust-hello-gcc-musl Hello, world!
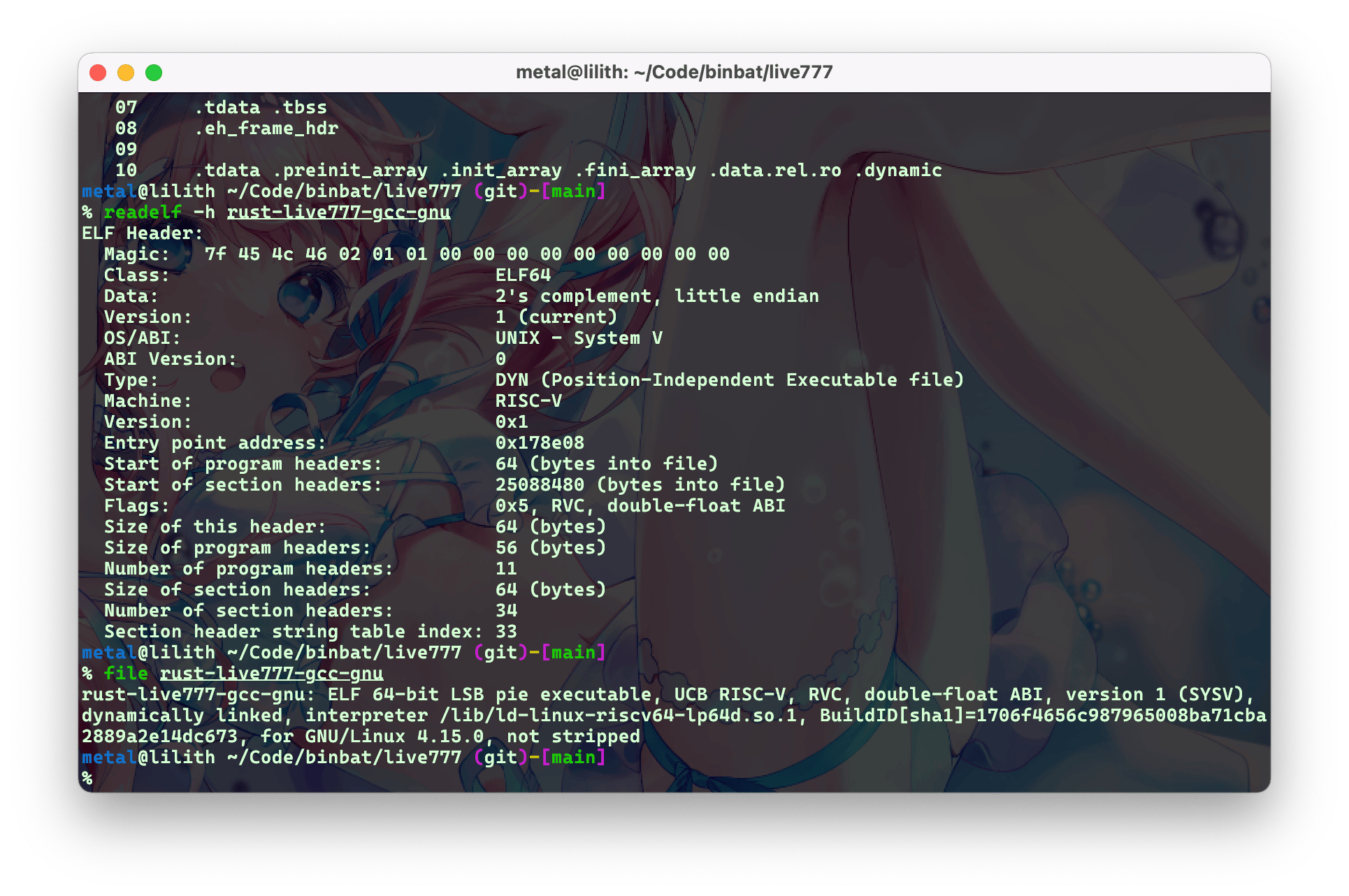
我们拿一个实际的项目试试,用 patchelf 来修改 glibc 版本的 live777 试试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 % cp target/riscv64gc-unknown-linux-musl/release/live777 rust-live777-gcc-musl % cp target/riscv64gc-unknown-linux-gnu/release/live777 rust-live777-gcc-gnu % cp target/riscv64gc-unknown-linux-gnu/release/live777 rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf % readelf -d rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf | grep NEEDED 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libgcc_s.so.1] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libm.so.6] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libc.so.6] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [ld-linux-riscv64-lp64d.so.1] % patchelf --set-interpreter /lib/ld-musl-riscv64.so.1 rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf % patchelf --replace-needed libc.so.6 libc.so rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf % patchelf --replace-needed libm.so.6 libc.so rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf % patchelf --replace-needed ld-linux-riscv64-lp64d.so.1 ld-musl-riscv64.so.1 rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf % readelf -d rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf | grep NEEDED 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libgcc_s.so.1] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libc.so] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [libc.so] 0x0000000000000001 (NEEDED) Shared library: [ld-musl-riscv64.so.1]
移花接木大法搞出来的 live777 不能正常运行的,看起来用了 glibc 专有的函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 % ./rust-live777-gcc-gnu -sh: ./rust-live777-gcc-gnu: not found % ./rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf Error relocating ./rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf: gnu_get_libc_version: symbol not found Error relocating ./rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf: __res_init: symbol not found Error relocating ./rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf: __register_atfork: symbol not found Error relocating ./rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf: gnu_get_libc_version: symbol not found Error relocating ./rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf: __res_init: symbol not found Error relocating ./rust-live777-gcc-gnu-elf: __register_atfork: symbol not found % ./rust-live777-gcc-musl 2025-04-16T22:03:47.280021Z WARN ThreadId(01) live777: src/main.rs:25: set log level : info 2025-04-16T22:03:47.280936Z INFO ThreadId(01) live777: src/main.rs:31: Server listening on 0.0.0.0:7777
总结
使用 file 命令判断是否为静态链接还是比较靠谱的
ldd 依赖 /lib/ld ,全静态链接不走 ld ,而且没法跨 libc 和架构纯 rust,默认 gnu 和 musl 的 libc 都是动态链接,需要 RUSTFLAGS="-C target-feature=+crt-static" 来编译静态链接
zig 默认参数,zig 默认 gnu 为动态链接,musl 为静态链接
zig 配合 rust 处理交叉编译非常好用
cross-rs 也很好用
不要用 patchelf 来移植不同的 libc
Reference 计算机那些事(4)——ELF文件结构
计算机那些事(5)——链接、静态链接、动态链接
计算机那些事(6)——可执行文件的装载与运行
Executable and Linkable Format - Wikipedia
ldd (Unix) - Wikipedia
ldd 命令
记一次Rust静态编译
How to generate statically linked executables?
1721-crt-static - The Rust RFC Book